Here is a primer on how to migrate your organization’s services to the cloud.

By making their services available to enterprises, Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) have brought about a remarkable change in the approach to IT infrastructure needs and solutions. Cloud services are available for all technical needs, ranging from Big Data and IoT to mobile, analytics, and AI/ML. Be it a startup or a large enterprise, CSPs have offerings and services for all. In this journey of digital transformation, a cloud strategy is an enabler and may be initiated through many queries, such as:-
- How to identify the right CSP to meet the technical and business needs of an enterprise?
- Will platform/vendor lock-in be enforced if we go with one CSP?
- Will there be an adequate level of security and compliance enforcement?
- What will be the cost in the short/long-term and ROI?
- What will be the payback period for costs incurred?
- What are the maintenance and support requirements?
- Will we lose control of the system after migrating to the cloud?
- What are the required skillsets for cloud-based solutions and IT infrastructure?
- Which is better – engaging directly with CSPs, or using some cloud service aggregator or broker for providing the solutions?
Additionally, there can be queries on technical perspectives, such as:
- What are the cloud services that can be fitted to the solutions needed?
- Will a service of one CSP support similar services of another CSP?
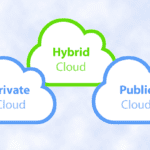
- Which is preferred – public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud infrastructure?
- How to utilize cloud services such as PaaS, IaaS, or SaaS?
There can be many such other questions while moving towards cloud
based infrastructure or solutions.
Cloud Enablement Challenges:-

An enterprise could face various challenges during cloud migration, even though it is aligned for migrating to cloud services.
These ground-level challenges can be the parameters for defining the success factor of its cloud enablement strategies. The following are some of the challenges faced by an enterprise during cloud migration.
- Adaption By People:-

For any enterprise, technology may not be the bottleneck; the highest level of challenges can come from people who take time to adapt to it.
- Strategies And Roadmap:-

Business objectives have to align with cloud strategies and define the roadmaps when moving forward.
Stockholders Consent is required to overcome the psychological bottlenecks in understanding cloud services.
People can be reluctant to move to cloud services due to their perceptions of
security, privacy, and technology.
- Existing Technical Encumbrances:-
These encumbrances should be identified, followed by the determination of a solution to make the move to cloud services. The legacy system should be analyzed, and a plan for migration to the cloud formulated.
- Training, Maintenance & Support:-

Training, maintenance, and support play an important part in cloud migrations. It is imperative to educate all personnel about the system and the advantages of using it. Employees have to be trained with the required skillsets. Overall
maintenance and support for the system is an ongoing process.
- ROI And Payback Period:-

The cost associated with cloud migration should be identified and fall within the budget of an enterprise. It is important to estimate the ROI and payback period.
- Technology Stack:-
Migration towards the right set of technologies plays an important role. A lot is changing around the world from the perspective of technology, and it is important to keep a measure of the right set of cloud services and solutions with a focus on the enterprise, people, and process capabilities to run for the long term.
- Security And Compliance:-

Security and compliance measures have to be identified and implemented with
cloud solutions.
- Downtime:-
There should be a near-to-zero downtime while migrating to cloud services. It should be at acceptable measures. Downtime can have a huge cost for any enterprise.
- Associated risk:-

Identification of proper risks before migration to the cloud is an important setup. There should be a proper mitigation plan for each of the identified risk areas. These risks can be technical, non-technical, operational, etc.
- Time To Market:-
Planning and identification of a cloud migration time frame, and mapping it with the ongoing enterprise business deliveries is challenging. This time
the frame is a significant contributor to decision making by enterprise stakeholders.
- Monitoring And Governance:-
Fear of lack of control after cloud migration can be a natural concern.
An enterprise is required to have the required in-house skillset to have
full control over cloud migration execution. Even the enterprise
data must be kept under complete control even though it may move to
a third party CSP. Identification of the right set of strategies is the first and key step towards cloud enablement for an enterprise. Cloud enablement strategies
should be mapped with enterprise business objectives and goals. It is important to measure the overall cloud enablement cost and prepare the
payback period and ROI details in the planning phase.
Cloud Transformation:-

Enterprise cloud enablement or transformation starts with the assessment
of the existing system of the enterprise. This assessment is required to be done at various levels, as listed below.
- Platform/Technology:-
Assessment of all duplicate/missing/legacy applications, tools, or frameworks
in the system. Assessment for repetitive manual work, systems or subsystems to retire, etc.
- Data:-
Assessment of data awareness gaps, data availability gaps, data analysis, etc. This is an important aspect to bring in the right value at the right time associated with the data in the system.
- People And Processes:–
Assessment of training requirements, management gaps, financial gaps, facility gaps, process inefficiencies, information gaps, measurement gaps, compliance needs, security needs, etc. The assessment of the different components of the enterprise will help to identify the existing cloud maturity level. Broadly, this can be categorized into three stages, as listed below:-
- Initial Stage:-
This involves enterprise planning for cloud enablement and working on various cloud strategies. The enterprise may have one or some of its applications on the cloud. It either has the following available or is working on these aspects:
- Cloud strategy and vision.
- Stakeholders’ alignment.
- Cloud enablement feasibility assessment.
- Cloud adoption roadmap.
- Training/workshops/sessions.
- Engaged Stage:-
In this stage, all major offerings are based on cloud solutions, and enterprises have the following:
- Enterprise policies for cloud enablement.
- Centre of excellence (cloud services/technologies).
- End-to-end solutions on the cloud.
- Round-the-clock services(governance, monitoring, management, security, compliance)
- Optimized stage:-
In this stage, the enterprise has developed the core
philosophy or strategy to go cloud-first for any of its infrastructure and
technology needs. It has incorporated the following in the system:-
- Highest satisfaction for its customers.
- Cloud-first.
- Optimisations (performance/cost).
- Research and development.
- Cloud-driven business innovations.
The Challenges And Solutions:-
However, the transformation to the cloud
may encounter a few challenges, such as:-
- Lack of awareness, knowledge, and confidence in cloud services capabilities
- Limited budget and executive support for cloud adoption
- Business-critical needs alignment with cloud adoption.
- Lack of direction for cloud adoption.
- Security and compliance establishment on the cloud.
- Availability of expert engineers/employees.
- TCO for cloud transformation.
- Optimizations for ongoing system monitoring, governance, and maintenance.
- Regular audits to establish all required security standards and compliance.
- Dependency on a single cloud provider.
- Innovative usage of cloud services.
- Expert cloud engineers in the staff.
These challenges can be addressed by taking certain actions:-
- Conducting sessions, training, and workshops for awareness, knowledge, and capabilities of cloud services.
- Comparison of services of various cloud providers
- Existing system assessment and audit
- Business needs alignment with cloud adoption recommendations
- Cloud adoption roadmap
- Implementation of various POC and feasibility checks for cloud
transformation.
- Referring to similar use cases, case studies, and success stories.
- Functional and non-functional needs feasibility check on identified cloud services.
- Education of employees for cloud services and their usage.
- System monitoring and further optimizations.
- Complete cloud transformation roadmap and plan.
- Establishment of a cloud center of excellence
- Security and compliance need assessment and recommendations.
- Available applications assessment for cloud transformation.
- Migration of applications to the cloud.
- Innovative applications and services implementation using cloud infra and services.
- Ongoing assessment of the latest cloud services for further optimization on performance or cost.
These action items can lead to outcomes like:-
- Cloud transformation strategies and roadmap.
- Confidence in cloud services capabilities.
- Business needs amalgamation for a solution on the cloud.
- Alignment with all stakeholders.
- Educated employees on cloud services management and maintenance.
- Cloud expert team.
- Best practices in place.
- Transformed people, processes, and platforms.
- Well established security, compliance, and governance processes.
- No dependency on a single cloud provider.
- High level of security and compliance establishment.
- Well defined processes, policies, and practices for cloud execution.
- The highest degree of customer satisfaction.
Cloud computing service models:-
It is important to understand the available cloud computing service
models while migrating to the cloud.
There are three cloud computing models — PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS
(Figure 1).
- PaaS:-
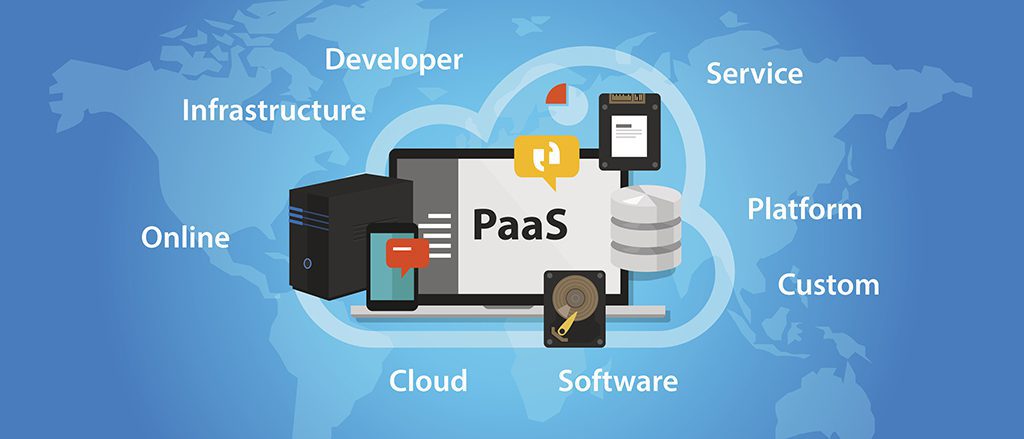
This cloud computing model facilitates the entire environment, which includes storage, servers, networking, OS, etc. Users can have their applications and data built on these platforms. Some of the examples
for PaaS are Force.com, Google App Engine, and Commerce Tools.
- IaaS:-
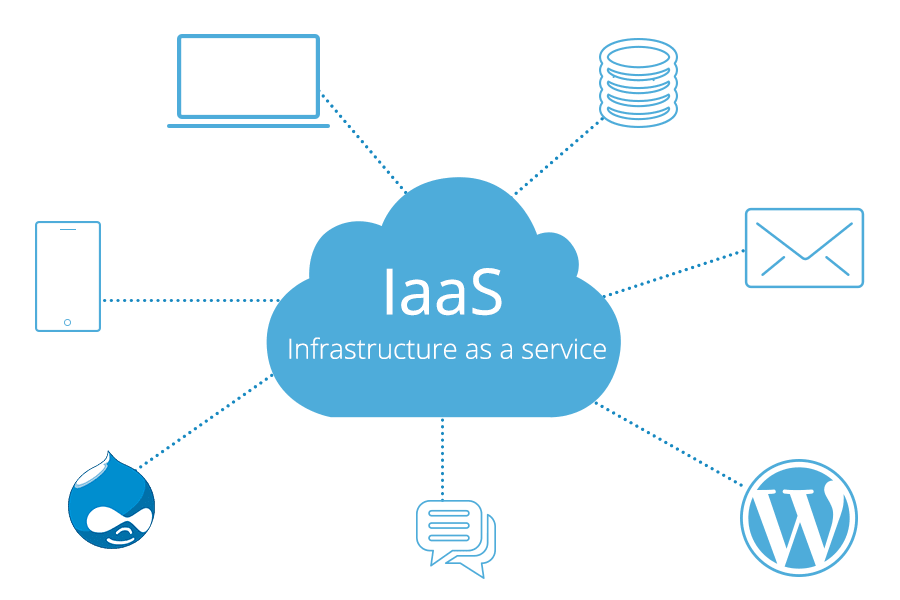
This provides an automated and scalable environment with flexibility and control over the system. Some of the examples for IaaS are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Rackspace, Google Cloud Engine, Microsoft Azure, Flexiscale, etc.
- SaaS:-
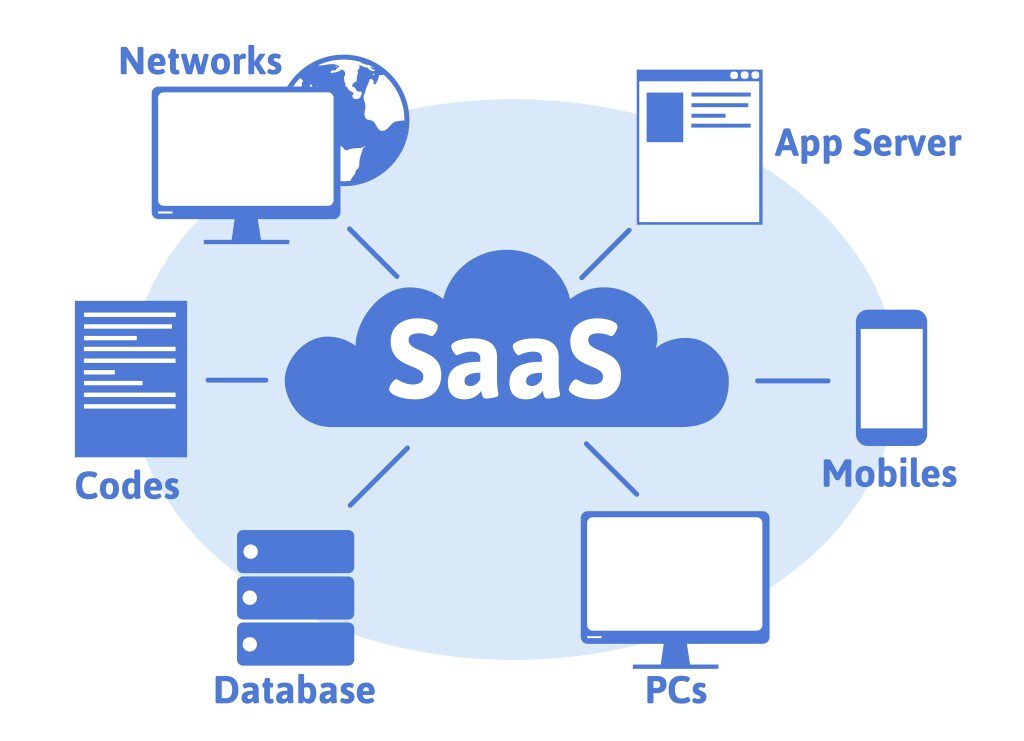
These are the applications available over the Internet.
Figure 2: Cloud computing models Users have less control over the customization or tailoring of features.
Some of the examples are Gmail, Google Doc, Citrix GoToMeeting, Cisco WebEx, etc.
Additionally, there are many other X-as-a-Service available like DaaS (Data-as-a-Service), SoaaS (Storage-as-a-Service), SeaaS (Security-as-a-Service), etc.
Enterprise cloud solutions are generally a combination of all these service models.
Cloud Deployment Models:-
There are some input parameters for identifying the right cloud computing
deployment forms like security needs, data management needs, and type of
data. The different forms of Cloud Computing is shown in Figure 2.
- Public Cloud:–
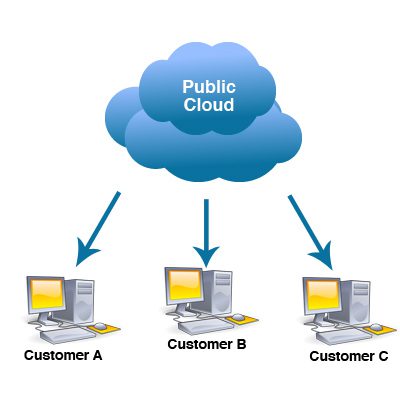
These cloud services are for generic usages and are hard
to customize as per the organization’s need. They work on a pay-per-use basis and are available over the Internet for everyone. Infrastructure resides under the control of the public cloud service provider, and the customers don’t have any control over data storage location, customization, etc. Some of the examples of public cloud services are E-mail, Google Docs, etc.
- Private Cloud:-
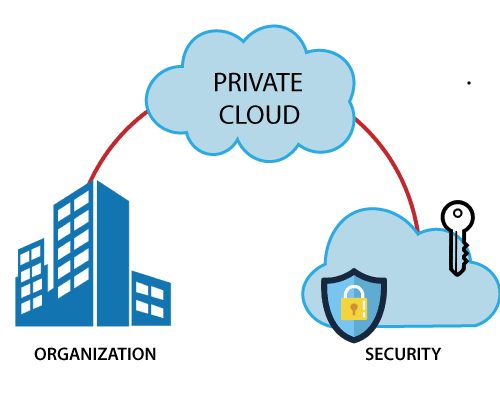
This cloud services setup is done as per the organization’s needs. It provides customization and secure access along with scalability as the business grows.
- Hybrid Cloud:-
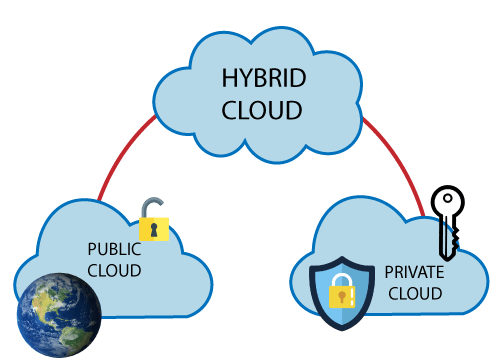
A hybrid cloud is an amalgamation of public or private cloud services and on-premise infrastructure. This provides an option to utilize best-of-breed services among those available from various CSPs.
It requires an effective level of integration between the services, and enforcement of the required security and management.
- Community Cloud:-
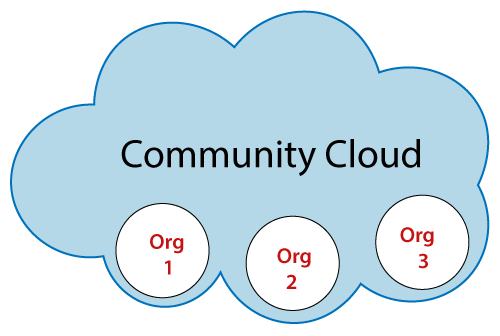
This is a shared infrastructure specific to a community. It is a multi-tenant
shared common platform between communities of similar needs,
concerns, security, compliance, etc.
Government departments, universities, and central banks are some of the examples of community cloud users.
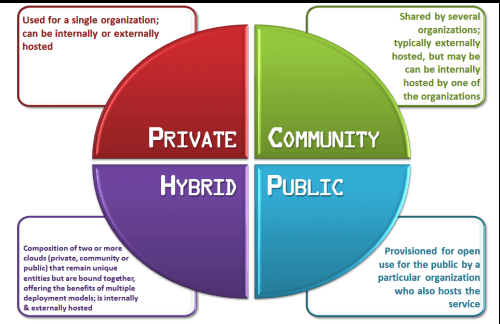
(Figure 02: Cloud Computing Models).
Evaluation Parameters Of Solutions:-
Figure 03 gives the parameters that need to be considered before opting for a cloud computing solution.
- Computing:-
The enterprise’s computing needs like managed instances, edge computing,
serverless computing, etc.
- Storage And Database:-
The enterprise’s storage and database needs like structured and
unstructured data, archival storage, data lake, etc.
- Infrastructure And Networking:-
The organization’s infrastructure and networking need like virtual network, gateways, VPN, etc.
- Application Services:-
The enterprise’s application services need like analytics, development
tools, integration tools, etc.
- Management And Governance:-
The enterprise’s management and governance needs like application monitoring and logs, infrastructure monitoring, usage reports, alter/ notification, configurations, etc.
- Security, Identity, And Compliance:-
The enterprise’s security, identity, and compliance needs like authentication,
authorization, role and privilege management, compliance enablement, security enforcement, etc.
These defined parameters consider various functional and non-functional aspects as well:-
Non-Functional Aspects: –
Availability, recoverability, resilience, security, data integrity, capacity, manageability, scalability, threat management, usability, performance, reliability, maintainability, interoperability, risk management, survivability,
disaster recovery, regulatory, etc.
Functional Aspects: –
Application features, transactions, administration, authentication, authorization, tracking, external interfaces, compliance, reporting,
certifications, historical data, governance, business rules, audit,
legal or regulatory, etc.
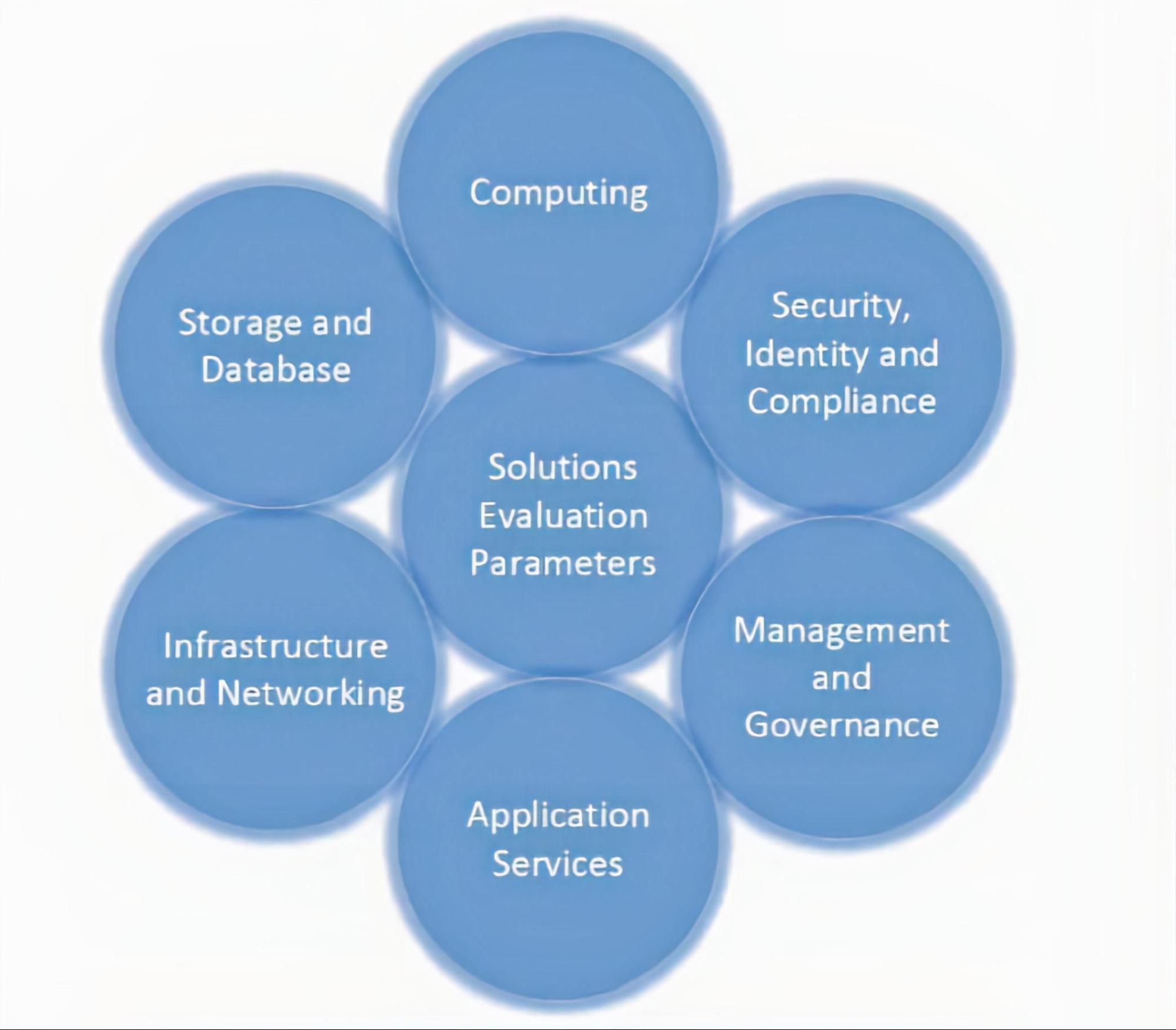
(Figure 03:- Parameters for consideration before choosing a cloud computing solution).